How molecular mechanisms of endoplasmic reticulum stress and drug resistance interact in leukemia cells
Simona Kureková, Lucia Pavlíková, Mario Šereš, Viera Boháčová, Albert Breier, Zdena Sulová
Research has shown that the proteins wolframin, P-glycoprotein (P-gp), and chaperone GRP78/BiP can collectively influence the response of leukemia cells to chemotherapy by regulating endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress. The ER ensures the proper folding and modification of proteins; its stress can lead either to the activation of cell survival mechanisms and the development of drug resistance, or, with prolonged exposure, to apoptosis and increased sensitivity to treatment. The study used L1210 mouse leukemia cells, which are drug-sensitive and resistant with high P-gp expression. Resistant cells showed increased levels of both GRP78/BiP and wolframin. Immunoprecipitation analyses confirmed the interaction of wolframine with GRP78/BiP, enhanced under ER stress conditions, as well as its binding to PERK and ATF6 receptors. The results suggest that ER stress regulation is closely linked to drug resistance mechanisms and may represent a potential therapeutic target.
KUREKOVÁ, Simona* – PAVLÍKOVÁ, Lucia* – ŠEREŠ, Mário* – BOHÁČOVÁ, Viera – ŠPALDOVÁ, Jana – BREIER, Albert** – SULOVÁ, Zdena**. Do wolframin, P-glycoprotein, and GRP78/BiP cooperate to alter the response of L1210 cells to endoplasmic reticulum stress or drug sensitivity? In Cancer Cell International, 2025, vol. 25, no. 1, art. no. 35. (2024: 6 – IF, Q1 – JCR, 1.5 – SJR, Q1 – SJR).
Daily rhythm of cell proliferation in the brain of songbirds
Ľubica Niederová-Kubíková, Vladimíra Hoďová, Valentína Marešová, Rebecca Radič
New neurons are created in the brains of both young and adult individuals. Their creation is influenced by many factors, including physical activity and the circadian system, which is synchronized by light. Neurogenesis in laboratory rodents is highest during the dark phase of the day, similar to their activity. However, in animals that are active during the light phase of the day, it is not known whether brain cell formation follows a daily rhythm and when it peaks. In this study, we found that in adult red-winged blackbirds (Taeniopygia guttata), the expression of clock gene mRNA showed a circadian rhythm, whereas the formation of new cells throughout the brain did not. However, in the “hot spot” area, i.e., the area of most intense cell division, new cell formation had rhythmic activity with a 24-hour period, peaking at the beginning of the dark phase. Apoptotic gene expression did not show a rhythmic pattern. This study is important for understanding the mechanisms that regulate the formation of new cells in the brain across various species, including humans.
HOĎOVÁ, Vladimíra – MAREŠOVÁ, Valentína – RADIČ, Rebecca – KUBÍKOVÁ, Ľubica**. A daily rhythm of cell proliferation in a songbird brain. In Scientific Reports, 2025, vol. 15, no. 1, art. no. 4685. (2024: 3.9 – IF, Q1 – JCR, 0.874 – SJR, Q1 – SJR). ISSN 2045-2322.
Occurrence of extended-spectrum β-lactamases and monoresistance to ertapenem in Escherichia coli strains isolated from calves with diarrhea.
Lívia Karahutová, Dobroslava Bujňáková
The resistance of the Enterobacterales family to carbapenems, fluoroquinolones, and polymyxins is a key point in the WHO’s concept for combating antimicrobial resistance. In human medicine, carbapenems are considered the “last resort” for treating multidrug-resistant infections, but they are banned in veterinary medicine. Nevertheless, there has been an increase in carbapenem-resistant strains due to “co-selection” caused by the excessive use of other β-lactam antibiotics. In our study, we focused on assessing the antibiotic resistance of Escherichia coli isolated from calves with diarrhea. High levels of resistance were observed to penicillins, tetracyclines, fluoroquinolones, sulfonamides, and aminoglycosides. 71% of isolates showed multidrug resistance. The isolated occurrence of resistance to 4th-generation cephalosporins and ertapenem (carbapenems) is concerning. The presence of mobile elements (int1, tn3) and the blaCMY-2, blaCTX-M-1, blaCTX-M-2 , and blaCTX-M-9 genes confirms the potential for horizontal spread of resistance.
KARAHUTOVÁ, Lívia – BUJŇÁKOVÁ, Dobroslava**. Occurrence of extended- spectrum β-lactamases and ertapenem- mono- resistance in Escherichia coli isolated from diarrheal calves. In One Health, 2025, vol. 21, art. no. 101138. (2024: 4.5 – IF, Q1 – JCR, 1.202 – SJR, Q1 – SJR). ISSN 2352-7714.
Enterocin substance (Ent)7420, a new postbiotic for maintaining growth, immunity, and intestinal health in rabbits infected with MRSE
Monika Pogány Simonová, Jana Ščerbová, Katarína Tokarčíková, Ľubomíra Grešáková, Iveta Plachá, Andrea Lauková
The high rate of colonization of methicillin-resistant (MR) staphylococci in healthy farm animals poses a risk to human health due to contamination of animal products. Enterocin substances-Ent, antimicrobial proteins produced by some enterococci, can improve animal health and product quality when used as feed additives. Therefore, a pathogenic environment was simulated by applying the MR strain Staphylococcus epidermidis (MRSE) and monitoring its effects on the growth, immunity, and intestinal health of rabbits, as well as the protective effect of Ent7420 when administered together. The MRSE strain did not negatively affect growth and immunity, but it did worsen the morphology of the animals’ intestinal epithelium. After the application of Ent7420, growth improved, immunity was stimulated in healthy rabbits, and the damaging effects of the MRSE strain on intestinal health in infected rabbits were mitigated. The results indicate the promising use of Ent7420 to promote growth and immunity in animals, as well as its protective effect against staphylococcal infections in rabbit breeding.
POGÁNY SIMONOVÁ, Monika** – CHRASTINOVÁ, Ľubica* – ŠČERBOVÁ, Jana – TOKARČÍKOVÁ, Katarína – GREŠÁKOVÁ, Ľubomíra – ŽITŇAN, Rudolf – PLACHÁ, Iveta – LAUKOVÁ, Andrea*. Enterocin Ent7420 – a potential postbiotic additive: effect on growth, immune response and gut health in MRSE-infected rabbits. In Frontiers in Veterinary Science, 2025, vol. 12, art. no. 1330371. (2024: 2.9 – IF, Q1 – JCR, 0.783 – SJR, Q1 – SJR, karentované – CCC). (2025 – Current Contents). ISSN 2297-1769.
Development of transport systems based on metal-organic frameworks for bioimaging and targeted therapy
Mariana Máčajová, Majlinda Meta, Boris Bilčík, Ivan Čavarga, Veronika Huntošová
The set of published works focuses on the synthesis and characterization of surface-modified metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) as multifunctional drug nanocarriers. MIL-101(Al)–NH? was used to deliver hypericin, a well-known antiviral and antibacterial agent. The complex inhibited the interaction between the SARS-CoV-2 protein and ACE2 receptors, exhibited antibacterial activity, and showed an immunostimulatory effect, a characteristic of MOF itself. In an in vitro bacterial and ex ovo model of bacterial infection on the chorioallantoic membrane of a quail embryo, the possibility of delivering an antibiotic and photosensitizer to overcome bacterial resistance using photodynamic therapy was demonstrated. MOFs can be functionally modified (UiO-66 nanoparticles loaded with histidine) to deliver 5-fluorouracil to tumor cells. The results highlight MOFs as promising nanoplatforms for multimodal therapy – antiviral, antibacterial, immunomodulatory, and targeted chemotherapy, or photodynamic therapy.
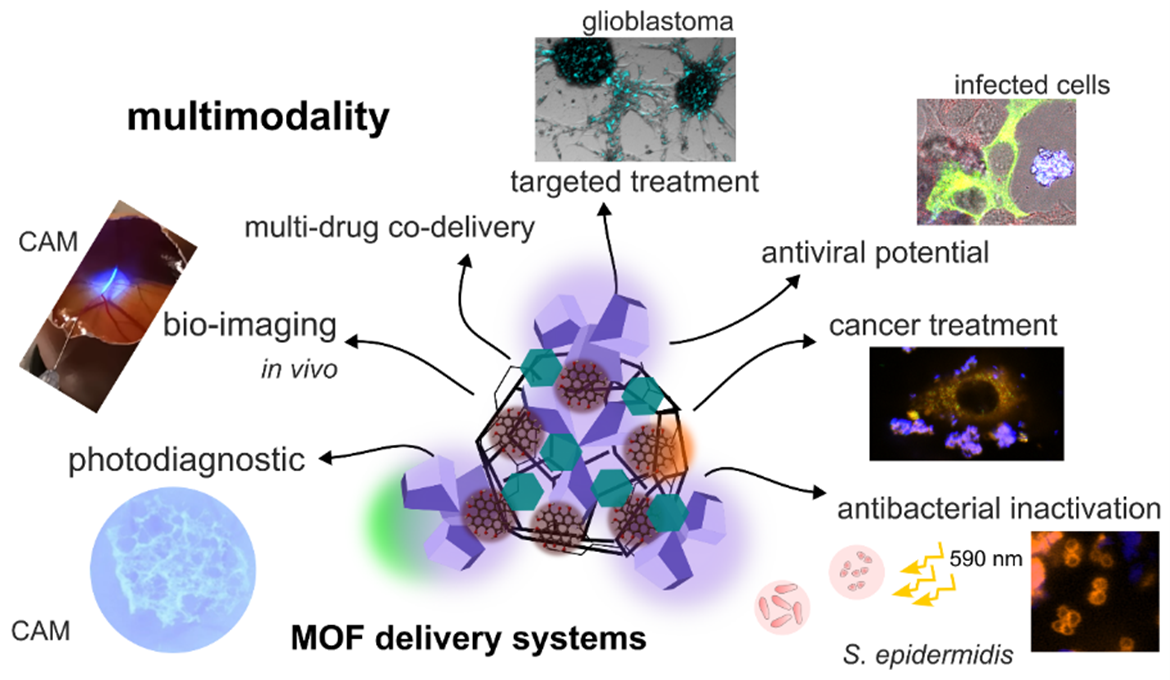
HUNTOŠOVÁ, Veronika** – BENZIANE, Anass – ZAUŠKA, Ľuboš – AMBRO, Ľuboš – OLEJÁROVÁ, Soňa – JONIOVÁ, Jaroslava – HLÁVKOVÁ, Nina – WAGNIERES, Georges – ZELENKOVÁ, Gabriela – DIKO, Pavel – BEDNARČÍK, Jozef – ZÁKÁNY, Florina – KOVÁCS, Tamás – SEDLÁK, Erik – VÁMOSI, György – ALMÁŠI, Miroslav**. The potential of metal-organic framework MIL-101(Al)-NH2 in the forefront of antiviral protection of cells via interaction with SARS-CoV-2 spike RBD protein and their antibacterial action mediated with hypericin and photodynamic treatment. In Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2025, vol. 691, art.no. 137454. (2024: 9.7 – IF, Q1 – JCR, 1.885 – SJR, Q1 – SJR)
MIGASOVÁ, Alexandra – ZAUŠKA, Ľuboš – ZELENKA, Tomáš – VOLAVKA, Dominik – FÉROVÁ, Marta – GULYÁSOVÁ, Terézia – TOMKOVÁ, Silvia – SALÁKOVÁ, Michaela – KUCHÁROVÁ, Veronika – SAMUELY, Tomáš – BEDNARČÍK, Jozef – SLABÝ, Cyril – MÁČAJOVÁ, Mariana – BILČÍK, Boris – SCHUBERT, Tim – WALTER, Andreas – HORNEBECQ, Virginie – HUNTOŠOVÁ, Veronika** – ALMÁŠI, Miroslav**. Histidine-modified UiO-66(Zr) nanoparticles as an effective pH-responsive carrier for 5-fluorouracil drug delivery system: A possible pathway to more effective brain cancer treatments. In Chemical Engineering Journal, 2025, vol. 522, art. no. 167857. (2024: 13.2 – IF, Q1 – JCR, 2.696 – SJR, Q1 – SJR)
MÁČAJOVÁ, Mariana – AMBRO, Ľuboš – META, Majlinda – ZAUŠKA, Ľuboš – GULYÁSOVÁ, Terézia – BILČÍK, Boris – ČAVARGA, Ivan – ZELENKOVÁ, Gabriela – SEDLÁK, Erik – ALMÁŠI, Miroslav** – HUNTOŠOVÁ, Veronika**. The Immunostimulatory Effect of MIL-101(Al)-NH2 In Vivo and Its Potential to Overcome Bacterial Resistance to Penicillin Enhanced by Hypericin-Induced Photodynamic Therapy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2025, vol. 26, art. no. 11681. (2024: 4.9 – IF, Q1 – JCR, 1.27 – SJR, Q1 – SJR)
Acquired resistance to decitabine associated with the A180P deoxycytidine kinase mutation: Impact on the sequence of hypomethylating agents in the treatment of myeloid malignancies
Kristína Šimoničová, Ľuboš Janotka, Helena Kavcová, Ivana Borovská, Zdena Sulová, Albert Breier, Lucia Messingerová
The drugs decitabine (DAC) and azacitidine (AZA) improve survival in older patients with high-risk myelodysplastic syndrome and acute myeloid leukemia, but resistance often develops with repeated administration. In a previous study, we showed that resistance to AZA is often associated with reduced DAC efficacy. Conversely, our results in cell lines suggest that DAC-resistant cells mostly retain sensitivity to AZA. In models of DAC resistance, we identified a new mutation in the deoxycytidine kinase enzyme that leads to its rapid degradation and prevents DAC activation, whereas AZA does not utilize this enzyme. The results suggest that the order of administration of these drugs can significantly affect treatment efficacy. Since treatment in clinical studies often begins with AZA and then switches to DAC, this may lead to ineffective subsequent therapy. We therefore suggest investigating the reverse treatment order. However, DAC is not yet used in Slovak healthcare, although it is approved by the EMA.
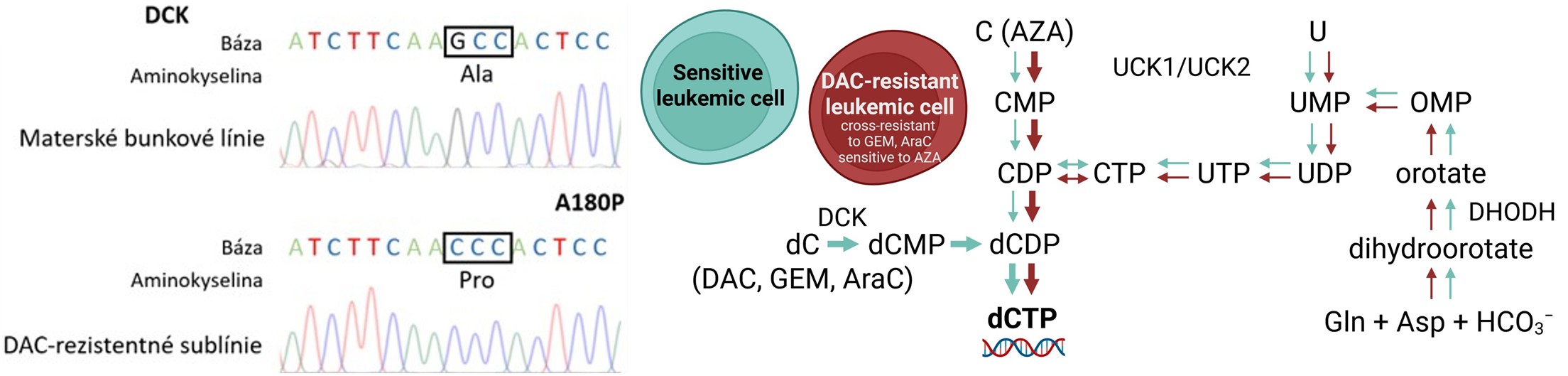
ŠIMONIČOVÁ, Kristína – JANOTKA, Ľuboš – KAVCOVÁ, Helena – BOROVSKÁ, Ivana – SULOVÁ, Zdena – BREIER, Albert** – MESSINGEROVÁ, Lucia**. Acquired Resistance to Decitabine Associated with the Deoxycytidine Kinase A180P Mutation: Implications for the Order of Hypomethylating Agents in Myeloid Malignancies Treatment. In International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2025, vol. 26, no. 11, art. no. 5083. (2024: 4.9 – IF, Q1 – JCR, 1.273 – SJR, Q1 – SJR).
Definition of positive animal welfare
Ľubor Košťál
An interdisciplinary team of scientists from 23 institutions in 15 countries working on the COST Lift project has proposed and published a definition of positive animal welfare. For decades, animal welfare science has focused primarily on the negative aspects of animal life, such as fear, pain, or suffering. This groundbreaking consensus defines positive animal welfare as flourishing (a term used in positive psychology) through predominantly positive mental states and the development of competencies and resilience. Positive welfare goes beyond ensuring good physical health and preventing and alleviating suffering. Positive mental states result from rewarding experiences, including choices and opportunities to actively pursue goals and achieve desired outcomes. The new definition provides a basis for a more comprehensive understanding of animal welfare, and judging by its reception in the less than a year since its publication, it has generated considerable interest in the scientific community (as of October 2025, according to WOS, this article ranked in the top 1% based on the threshold of frequently cited articles for the field and year of publication in the academic field of plant and animal sciences).

RAULT, Jean-Louis** – BATESON, Melissa – BOISSY, Alain – FORKMAN, Bjorn – GRINDE, Bjorn – GYGAX, Lorenz – HARFELD, Jess Lynning – HINTZE, Sara – KEELING, Linda – KOŠŤÁL, Ľubor – LAWRENCE, Alistair B. – MENDL, Michael T. – MIELE, Mara – NEWBERRY, Ruth C. – SANDOE, Peter – ŠPINKA, Marek – TAYLOR, Alex H. – WEBB, Laura E. – WHALIN, Laura – JENSEN, Margit Bak. A consensus on the definition of positive animal welfare. In Biology Letters, 2025, vol. 21, no. 1, art. no. 20240382. (2024: 3 – IF, Q2 – JCR, 1.071 – SJR, Q1 – SJR). ISSN 1744-9561.
Chicory modulates the rumen environment in lambs with endoparasites
Daniel Petrič, Matej Leško, Klára Demčáková, Zora Váradyová
Natural meadow and pasture ecosystems host a rich diversity of plant species, which serve as an important source of nutrients for grazing ruminants. The aim of the study was to evaluate the rumen environment of lambs with endoparasites grazed on meadow pastures enriched with experimentally sown chicory (Cichorium intybus). Lambs infected with larvae of the endoparasite Haemonchus contortus were divided into two groups: those grazed on a species-rich meadow pasture and those grazed on a pasture recultivated with chicory. The average initial weight of lambs was comparable in both groups until day 62 after infection, whereas from day 89 after infection, a significantly higher weight was recorded in the chicory group. The results confirmed the beneficial nutritional properties of chicory, as evidenced by changes in rumen microbiota and hydrolase activity, an increase in ammonia nitrogen concentration, and improved nutrient utilization, all of which positively affected the nutritional status and welfare of parasitically infested lambs.
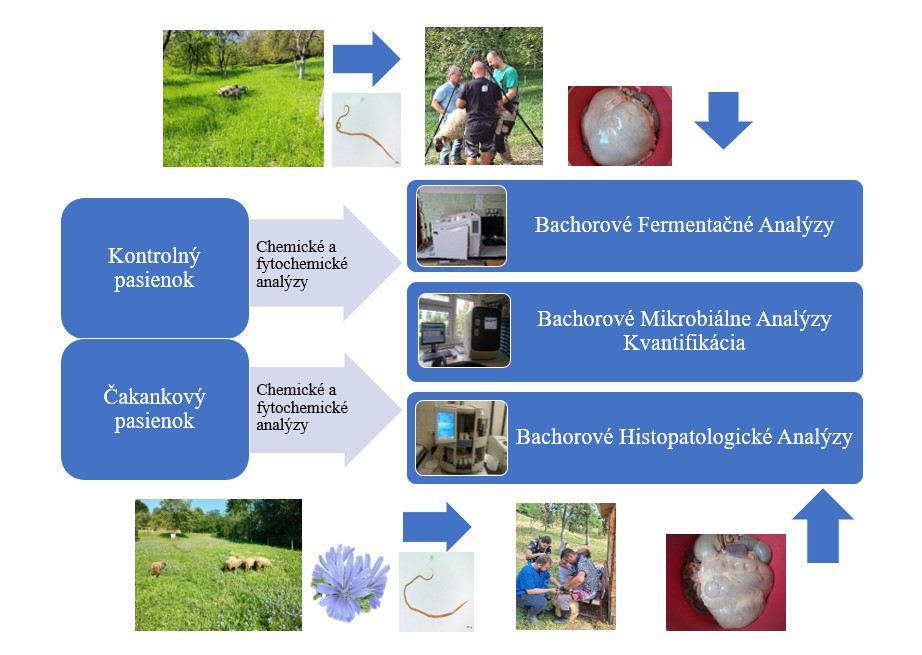
PETRIČ, Daniel – LEŠKO, Matej – DEMČÁKOVÁ, Klára – KOMÁROMYOVÁ, Michaela – ŚLUSARCZYK, Sylwester – KRAUZE, Izabela – ŁUKOMSKA, Anna – PAWLAK, Piotr – SIDORUK, Pola – CIESLAK, Adam – VÁRADY, Marián** – VÁRADYOVÁ, Zora**. Chicory modulates the rumen environment in lambs with endoparasites. In Scientific Reports, 2025, vol. 15, art. no. 35455. (2024: 3.9 – IF, Q1 – JCR, 0.874 – SJR, Q1 – SJR). ISSN 2045-2322.
Functional characterization of a new pathogenic variant of the CACNA1C gene in a patient with neurodevelopmental disorder
APVV-21-0210
Bohumila Jurkovičová Tarabová, Norbert Weiss
The CACNA1C gene encodes the CaV1.2 calcium channel, which is crucial for heart and brain function. Its mutations are associated with neurodevelopmental and cardiac disorders, including Timothy syndrome. Our study characterizes a de novo mutation in the CACNA1C gene identified in a pediatric patient. Our study characterizes a de novo mutation in the CACNA1C gene identified in a pediatric patient. It is a heterozygous missense variant (c.1973T > C; L658P) that manifested as severe drug-resistant epilepsy, developmental delay, and hypotonia, but without cardiac involvement. Electrophysiological analysis revealed a significant shift in the voltage dependence of channel activation/inactivation toward more negative potentials. Molecular modeling suggested that the mutation disrupts interactions in the IIS5 transmembrane segment, facilitating transitions between channel states and channel opening at more negative membrane potentials. These findings confirm that L658P is a pathogenic variant in the CACNA1C gene, primarily associated with severe neurological disorders, and highlight the broader significance of CaV1.2 channels in these disorders.
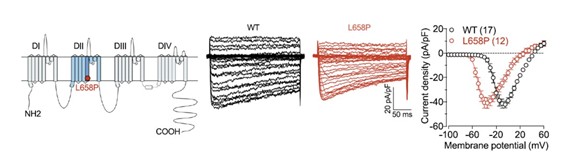
STRINGER, Robin N. – TANG, Xuechen – JURKOVIČOVÁ TARABOVÁ, Bohumila – MURPHY, Mary – LIEDL, Klaus R. – WEISS, Norbert**. Functional characterization of a novel de novo CACNA1C pathogenic variant in a patient with neurodevelopmental disorder. In Molecular Brain, 2025, vol. 18, no. 1, art. no. 26. (2024: 2.9 – IF, Q2 – JCR, 1.191 – SJR, Q2 – SJR).




