- Significant scientific results 2023
- Significant scientific results 2022
- Significant scientific results 2021
- Significant scientific results 2020
- Significant scientific results 2019
- Significant scientific results 2018
- Significant scientific results 2017
2024
Processes related to the maturation of bull sperm
Jana Jankovičová, Katarína Michalková, Petra Sečová, Ľubica Horovská, Jana Antalíková
For sperm released from the testis to acquire the ability to fertilize an oocyte, they must undergo modifications in the epididymis environment. These modifications include changes to the plasma membrane (PM), as well as to the glycocalyx, which is composed of glycoproteins and glycolipids. We characterized these changes in epididymal spermatozoa and PM fractions. Meanwhile, spermatozoa can incorporate new molecules via extracellular vesicles (EVs) from epididymal fluid and seminal plasma. Tetraspanins (TSPNs) are used as EV markers. Our analyses revealed the presence of TSPN CD63 in bull testes and epididymal tissues, in EVs produced in these organs, on epididymal spermatozoa, and after ejaculation. We found distinct distributions of potential CD63 partners, such as CD9, integrin αV, and syntenin-1, on the sperm head and flagellum, as well as in EVs. These findings highlight the need to analyze not only the molecular profile of EVs, but also their sublocalization on spermatozoa. This opens new possibilities for their use in reproductive technologies.
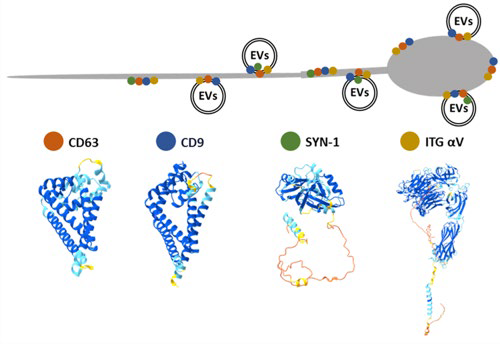
JANKOVIČOVÁ, Jana** – MICHALKOVÁ, Katarína* – SEČOVÁ, Petra – HOROVSKÁ, Ľubica – ANTALÍKOVÁ, Jana. The extracellular vesicle tetraspanin CD63 journey from the tetraspanin CD63 journey from the mature bull sperm. In Scientific Reports, 2024, vol. 14, no., art. no. 29449. (2023: 3.8 – IF, Q1 – JCR, 0.9 – SJR, Q1 – SJR, karentované – CCC). (2024 – Current Contents, WOS, SCOPUS). ISSN 2045-2322.
SEČOVÁ, Petra – HACKEROVÁ, Lenka – HOROVSKÁ, Ľubica – MICHALKOVÁ, Katarína – JANKOVIČOVÁ, Jana – POSTLEROVÁ, Pavla** – ANTALÍKOVÁ, Jana**. Complexity and modification of the bull sperm glycocalyx during epididymal maturation. In Faseb Journal : official publication of the Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology, 2024, vol. 38, no. 10, art. no. 23687. (2023: 4.4 – IF, Q1 – JCR, 1.412 – SJR, Q1 – SJR). ISSN 0892-6638.
Sulforaphane and benzylisothiocyanate suppress cell proliferation and induce cell cycle arrest, autophagy and apoptosis in a human AML cell line
Anna Bertová, Szilvia Kontár, Martina Kšiňanová, Alberto Yoldi Vergara, Zdena Sulová, Albert Breier, Denisa Imrichová
Isothiocyanates (ITCs) are natural substances that have been proven to have cytotoxic activity on cancer cells. We investigated the effects of sulforaphane (SFN) and benzylisothiocyanate (BITC) on human acute myeloid leukemia SKM-1 cells and their P-glycoprotein-positive subvariant, SKM/VCR. We monitored the effects of SFN and BITC on cell proliferation, cell cycle progression, and apoptosis induction, analyzing changes in the levels of regulatory factors of these processes. A key finding was the concentration-dependent inhibition of the viability of both cell lines; BITC exhibited greater potency than SFN. SFN increased the proportion of cells in the G2/M phase. In contrast, BITC induced accumulation of cells in the sub-G1 phase and decreased levels of key cell cycle regulators. This suggests that BITC can overcome resistance mechanisms. BITC’s more pronounced apoptotic effect compared to SFN, even in P-gp-positive cells, is probably related to its higher lipophilicity. Both ITCs triggered autophagy as a defense mechanism in response to ITC-induced apoptosis.
BERTOVÁ, Anna – KONTÁR, Szilvia – KŠIŇANOVÁ, Martina – YOLDI VERGARA, Alberto – SULOVÁ, Zdena – BREIER, Albert – IMRICHOVÁ, Denisa. Sulforaphane and Benzyl Isothiocyanate Suppress Cell Proliferation and Trigger Cell Cycle Arrest, Autophagy, and Apoptosis in Human AML Cell Line. In International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2024, vol. 25, no. 24, art. no. 13511. (2023: 4.9 – IF, Q1 – JCR, 1.179 – SJR, Q1 – SJR). ISSN 1422-0067.
Molecular characterization and antibiotic resistance of Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus haemolyticus isolated from bovine mastitis
Dobroslava Bujňáková, Lívia Karahutová
Staphylococcal mastitis in cattle requires high treatment costs and poses a serious threat to public health due to the zoonotic potential of the causative agents. These bacteria exhibit pathogenicity through virulence-encoding genes, biofilm formation, and antibiotic resistance (AR).
Concerning staphylococcal ARs include β-lactam resistance and inducible macrolide-lincosamide-streptogramin B (iMLSB) resistance, both of which have been detected in our country. β-lactam resistance is encoded by the mec-negative blaZ gene, and iMLSB resistance is encoded by the msrA, ermC, and vgaA genes. Proper treatment requires identifying iMLSB because administering clindamycin can lead to treatment failure by causing constitutive iMLSB. Multi-resistant strains have also been reported.
Biofilm formation is associated with microbial surface component recognizing adhesive matrix molecules (MSCRAMMs) and the expression of polysaccharide capsules and toxins. We detected the clfA, sdrD, sdrE, fnbpB, bbp, isdA, isdB, and hla genes. Spa typing confirmed type 10035.
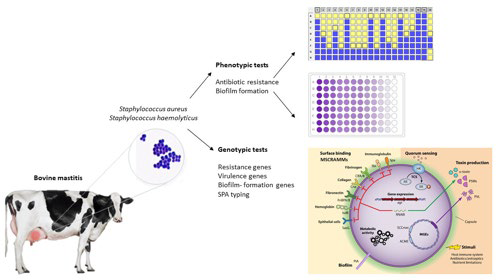
BUJŇÁKOVÁ, Dobroslava – KARAHUTOVÁ, Lívia. Molecular characteristics and antibiotic resistance of Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus haemolyticus isolated from bovine mastitis. In Research in Veterinary Science, 2024, vol. 177, art. no. 105365. (2023: 2.2 – IF, Q1 – JCR, 0.617 – SJR, Q1 – SJR).
Protective effect of enterocins for the preservation of rabbit meat quality
Monika Pogány Simonová, Eva Bino, Anna Kandričáková, Andrea Lauková
Rabbit meat is rich in essential amino acids (EAAs) and has the highest biological value of any meat. Despite efforts to maintain healthy rabbit production, infections often occur during rearing and affect the quality of the meat carcass. Enterocins (Ent), which are antimicrobial proteins produced by certain enterococci and used as feed additives, can improve animal health and increase the nutritional quality of rabbit meat. Therefore, a conditionally pathogenic environment was simulated by applying a biofilm-forming Enterococcus hirae Kr8+ strain to investigate its effect on rabbit growth and meat quality, as well as the protective effect of administered EntM when both substances were applied in combination. The Kr8+ strain did not negatively affect health, growth, or meat quality. On the contrary, higher weights and EAK levels in the meat were observed. EntM administration significantly improved growth parameters and EAA content (p < 0.001). Combined application of the two additives highlights the protective effect of EntM and represents their possible synergistic effect.
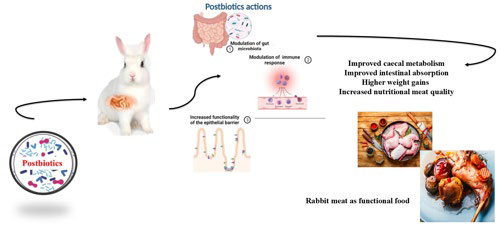
POGÁNY SIMONOVÁ, Monika** – CHRASTINOVÁ, Ľubica – BINO, Eva – KANDRIČÁKOVÁ, Anna – FORMELOVÁ, Zuzana – LAUKOVÁ, Andrea. Application of Autochthonous Biofilm-Forming Enterococcus hirae Kr8 Strain in Relation with Enterocin M in Broiler Rabbits and Their Effect on the Rabbit Meat Quality: Risk or Protection? In Probiotics and Antimicrobial Proteins, 2024, vol. 16, no. 3, pp. 1076-1086. (2023: 4.4 – IF, Q1 – JCR, 0.906 – SJR, Q2 – SJR).
Effect of valproic acid on mitochondrial functions
Paulína Horonyová, Ivana Ďurišová, Lenka Bábelová, Martin Valachovič, Mária Balážová
Impaired synthesis and remodeling of the essential phospholipid cardiolipin (CL) affects the structure and function of mitochondrial membranes. This leads to the development of cardiomyopathies and skeletal muscle myopathies, particularly in patients with Barth syndrome (BTHS). The main goals of the research were to understand mitochondrial dysfunctions caused by TAFAZZIN gene mutations and to test the therapeutic potential of valproic acid (VPA), a drug commonly used to treat neurological and psychiatric diseases. Results showed that subtherapeutic doses of VPA increased CL-dependent enzyme activity, improved oxidative phosphorylation, and increased ATP production. These positive effects were confirmed in both healthy cells and BTHS models, where VPA partially normalized mitochondrial function. This study sheds new light on the bioenergetics of BTHS and suggests VPA’s potential in treating mitochondrial diseases.
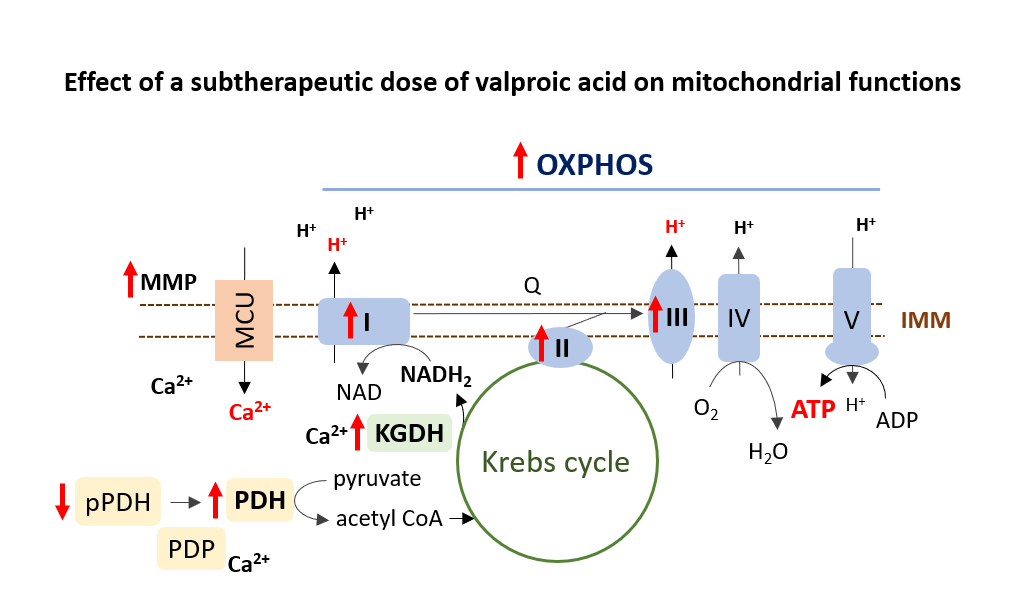
HORONYOVÁ, Paulína* – ĎURIŠOVÁ, Ivana* – ČERMÁKOVÁ, Petra – BÁBELOVÁ, Lenka – BUČKOVÁ, Barbora – ŠOFRANKOVÁ, Lucia – VALACHOVIČ, Martin – HSU, Yuan-Hao Howard – BALÁŽOVÁ, Mária. The subtherapeutic dose of valproic acid induces the activity of cardiolipin- 13 dependent proteins. In Biochimica et Biophysica Acta – Bioenergetics, 2024, vol. 1865, no. 4, art. no. 149501. (2023: 3.4 – IF, Q1 – JCR, 1.541 – SJR, Q1 – SJR). ISSN 0005-2728.
LIANG, Zhuqing – RALPH-EPPS, Tyler – SCHMIDTKE, Michael W. – LAZCANO, Pablo – DENIS, Simone W. – BALÁŽOVÁ, Mária – TEIXEIRA J, Nevton Da Rosa – CHAKKOUR, Mohamed – HAZIME, Sanaa – REN, Mindong – SCHLAME, Michael – HOUTKOOPER, Riekelt H. – GREENBERG, Miriam L.. Upregulation of the AMPK1-FOXO1-PDK4 pathway is a primary mechanism of pyruvate dehydrogenase activity reduction in tafazzin-deficient cells. In Scientific Reports, 2024, vol. 14, no. 1, art. no. 11497. (2023: 3.8 – IF, Q1 – JCR, 0.9 – SJR, Q1 – SJR). (2024 – Current Contents, WOS, SCOPUS). ISSN 2045-2322.
Early detection of diseases by aptasensors
Michaela Domšicová, Jana Korčeková, Albert Breier, Alexandra Poturnayová
The rapid and sensitive detection of biomarkers is important for the early prevention and treatment of diseases. The demand for more precise diagnostics has led to the development of aptasensors, which are biosensors that use aptamers. These stable, easily modifiable nucleic acids (DNA or RNA) bind with high affinity and specificity to biomarkers, overcoming some limitations of antibodies. Aptasensors convert the binding of the aptamer to the biomarker into a detectable signal, enabling accurate quantification. When integrated with mass-sensitive analytical techniques (QCM), aptasensors represent a significant advance in clinical research. Our investigations demonstrated the high sensitivity of the proposed aptasensors in detecting infectious diseases caused by the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus (LOD = 0.07 pg/mL) and recognizing chronic myeloid leukemia cells (LOD = 263 bb/mL). Both types of aptasensors have also been validated in body fluids, such as plasma or saliva, with high potency.
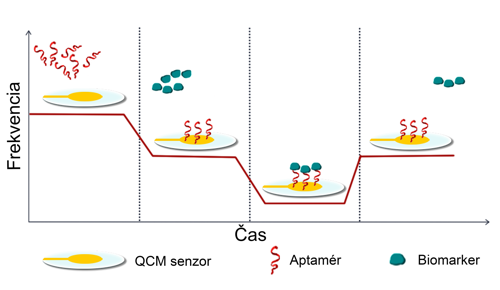
NEMČEKOVÁ, Katarína – KORČEKOVÁ, Jana – SVITKOVÁ, Veronika – BARANIAK, Denis – DOMŠICOVÁ, Michaela – MELNÍKOVÁ, Eva – HORNYCHOVÁ, Michaela – SZEBELLAIOVÁ, Viktória – GÁL, Miroslav** – POTURNAYOVÁ, Alexandra. Comparative Analysis of QCM and Electrochemical Aptasensors for SARS-CoV-2 Detection. In Biosensors, 2024, vol. 14, no. 9, art. no. 431. (2023: 4.9 – IF, Q1 – JCR, 0.707 – SJR, Q1 – SJR). ISSN 2079-6374.
DOMŠICOVÁ, Michaela – KUREKOVÁ, Simona – BÁBELOVÁ, Andrea – JAKIČ, Kristína – ORAVCOVÁ, Iveta – NÉMETHOVÁ, Veronika – RÁZGA, Filip – BREIER, Albert – GÁL, Miroslav** – POTURNAYOVÁ, Alexandra**. Advancements in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia detection: Development and evaluation of a novel QCM aptasensor for use in clinical practice. In Biochemistry and Biophysics Reports, 2024, vol. 39, no., art. no. 101816. (2023: 2.3 – IF, Q3 – JCR, 0.584 – SJR, Q2 – SJR). ISSN 2405-5808.
Influence of binding preferences of divalent ions by metalloproteins on the evolution of RNA editing and protein coding
Katarína Vondrášková, Jana Královičová
An extensive bioinformatic analysis of data obtained from proteomic, structural, and genomic databases, performed by the University of Southampton research group, and experimental validation, performed by the Centre for Biosciences research group, revealed that exons encoding amino acids that coordinate Zn²⁺ are supported by auxiliary downstream motifs significantly less frequently than exons encoding amino acids that coordinate Ca²⁺. However, Zn²⁺-coordinating exons are compensated for by stronger downstream sites and a polypyrimidine tract with a higher number of uridines. These results demonstrate that constraints on RNA downregulation imposed by metal-coordinating spheres can be effectively overcome by the plasticity of the exon-intron architecture, ensuring adequate metalloprotein expression.
BAKHTIAR, Dara – VONDRÁŠKOVÁ, Katarína – PENGELLY, Reuben – CHIVERS, Martin – KRÁLOVIČOVÁ, Jana – VOŘECHOVSKÝ, Igor**. Exonic splicing code and coordination of divalent metals in proteins. In Nucleic Acids Research, 2024, vol. 52, no. 3, p. 1090-1106. (2023: 16.6 – IF, Q1 – JCR, 7.048 – SJR, Q1 – SJR). ISSN 0305-1048.
Zinc supplementation in the form of nanoparticles affects rumen fermentation, microbial population and rumen histology in lambs
Daniel Petrič, Klaudia Čobanová, Zora Váradyová
Zinc nanoparticles improve the bioavailability of zinc in the body. In particular, due to the higher antimicrobial activity, which is related to the size of the nanoparticles in the subcellular range, rumen fermentation in small ruminants is affected. The nutrients required by ruminants for their nutrition and development are mostly derived from the rumen fermentation of polysaccharides in the feed and are absorbed through the rumen epithelium. We hypothesized that different zinc nanoparticles would affect rumen fermentation, microbiota as well as histology of the rumen of lambs to some extent both under in vitro conditions and under short-term (28 days) and long-term (70 days) supplementation in feed. In collaboration with colleagues at the Poznan University of Life Sciences, we found that supplementation with zinc nanoparticles improves feed utilization efficiency, but active microbial fermentation can affect rumen epithelial health in lambs regardless of the form, dose or duration of application. However, zinc nanoparticles are a promising nutritional supplement for sheep that may contribute to more efficient nutrient utilization and improved digestion.
PETRIČ, Daniel – MIKULOVÁ, Klára – BOMBÁROVÁ, Alexandra – BATŤÁNYI, Dominika – ČOBANOVÁ, Klaudia – KOPEL, Pavel – LUKOMSKA, Anna – PAWLAK, Piotr – SIDORUK, Pola – KOTWICA, Szymon – CIESLAK, Adam** – VÁRADYOVÁ, Zora**. Efficacy of zinc nanoparticle supplementation on ruminal environment in lambs. In BMC Veterinary Research, 2024, vol. 20, no., art. no. 425. (2023: 2.3 – IF, Q1 – JCR, 0.658 – SJR, Q1 – SJR). ISSN 1746-6148.
Phosphorylation of Sfr1 by CDK kinase reduces Rad51 function in invasion of homologs during late stages of meiotic recombination
APVV-21-0210
Silvia Bágeľová Poláková
Meiosis is a unique process involving homologous recombination and subsequent chromosome segregation that gives rise to genetically variable haploid cells. Our laboratory’s long-term goal is to identify and characterize novel genes that are essential for accurate chromosome segregation during meiosis. As part of a genome-wide gene screen, we discovered and characterized the dbl2 gene. In collaboration with Dr. Cristina Martín-Castellanos’s laboratory at the IBFG-CSIC-USAL in Spain, we elucidated this year how the phosphorylation of the Sfr1 protein by CDK kinase regulates the activity of the Rad51 recombinase in later stages of homologous recombination during meiosis. To confirm the mechanism of action of CDK kinase, we examined the phenotypic expression of the dbl2Δ deletion mutant, which is active at the same stage of homologous recombination as the Sfr1 protein. This discovery significantly contributes to our understanding of the mechanisms that control genetic stability during sexual reproduction.
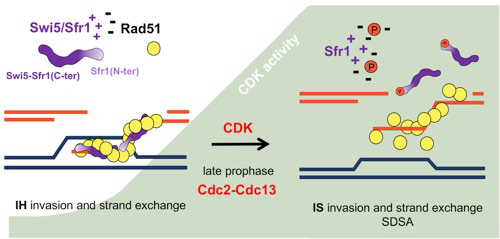
PALACIOS-BLANCO, Inés – GÓMEZ, Lucía – BORT, María – MAYEROVÁ, Nina – BÁGEĽOVÁ POLÁKOVÁ, Silvia – MARTÍN-CASTELLANOS, Cristina. CDK phosphorylation of Sfr1 downregulates Rad51 function in late-meiotic homolog invasions. In EMBO journal : European Molecular Biology Organization, 2024, vol. 43, no. 19, p. 4356-4383. (2023: 9.4 – IF, Q1 – JCR, 5.489 – SJR, Q1 – SJR). ISSN 0261-4189.




